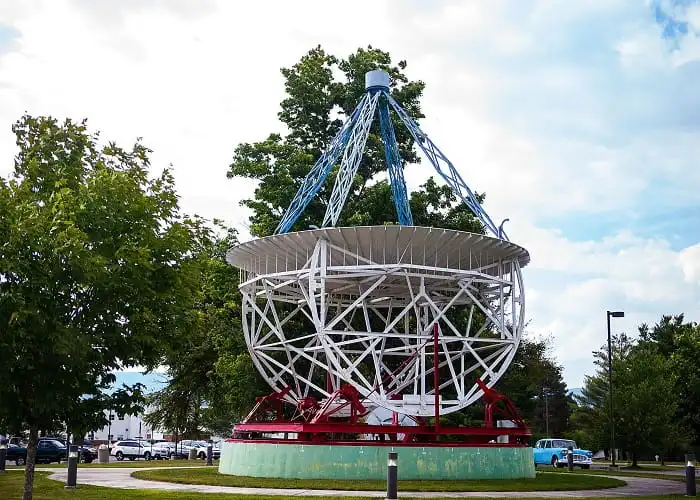
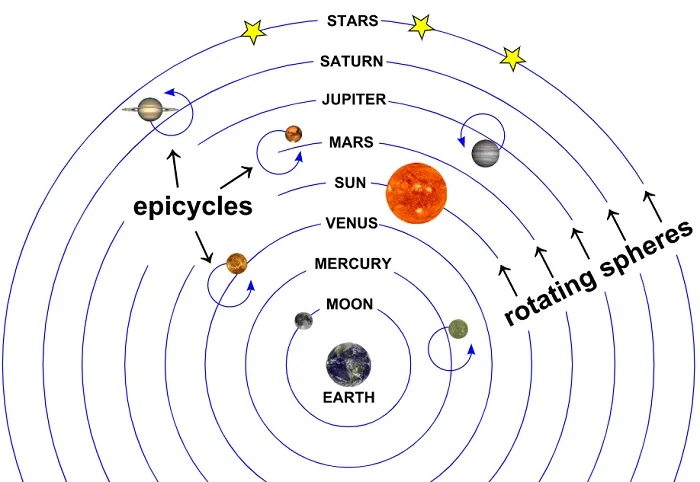
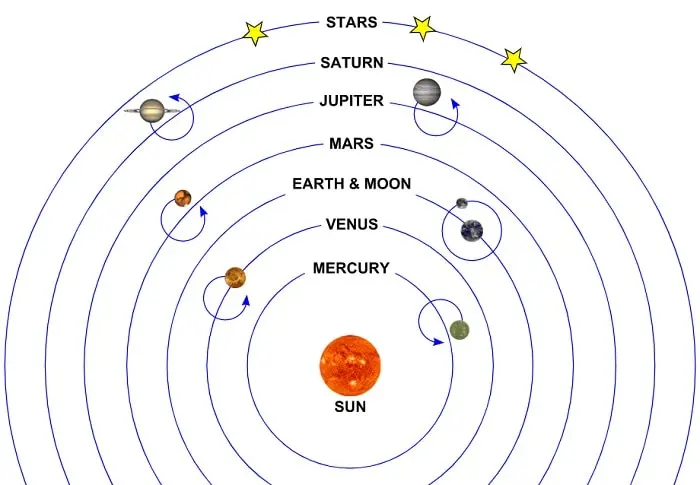
How and when did we discover what stars were? Our stargazing studies, or knowledge of the stars, have developed impressively since the Italian philosopher Giordano Bruno (1548–1600), who was imprisoned and burned for claiming that the sun is just one of the many stars (and that he had some other religious beliefs). However, the greatest leap would occur in the nineteenth century, when new scientific techniques such as parallax were developed, allowing us to determine spectral measurements and star distances.
Since the sun is very close to us from a universal perspective, we have obtained important information about other stars only by examining our own star. By looking at the different stars, each at a different stage of their evolution, astronomers gathered information about the life cycle of stars and understood how the sun and the solar system would reach their ultimate end.
Stargazing in Egypt
We now know what stars are made of, how hot they are, and how they move in space. However, the discoveries of brown dwarf stars and planets outside the Solar System have shown that there are many mysteries to be solved about the stars. In ancient Egypt, astronomy was very important, but for them, it was more like a religion than a science. The Hunter Constellation, for example, represented Osiris, the god of death. The following image, taken from a mummy coffin, depicts the daughter of the god Shu (the god of the atmosphere), and Nuit (the goddess of the sky), as she leaves Earth.
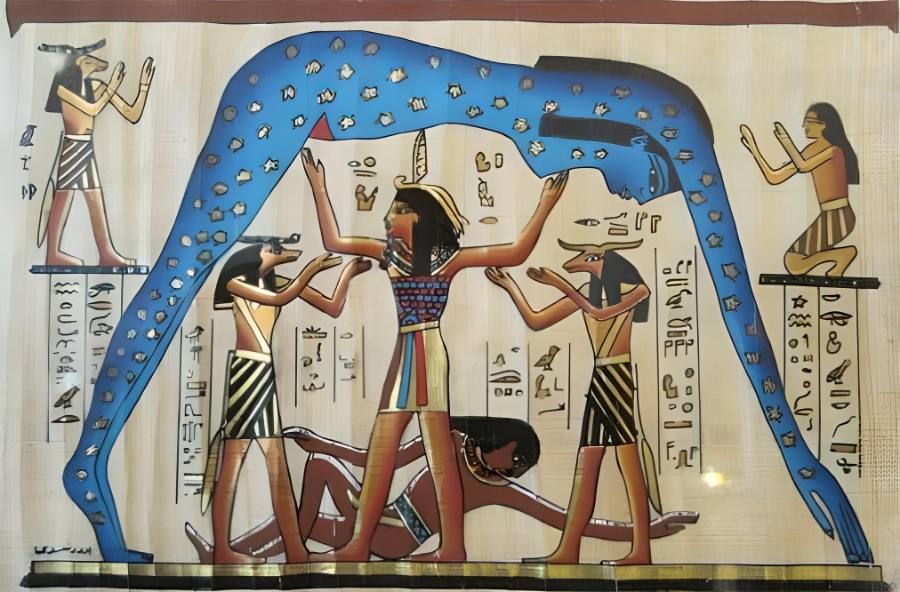

Stargazing in Babylon
The Babylon tablet below, which dates back to 500 BC, is covered with writings describing the movements of stars and planets. The Babylonians were intelligent astronomers and astrologers who could predict eclipses, invented the angular measure to find the angular distances of sky objects, and designed an effective form of numerical representation for all that.
A Babylon tablet describing the movements of the stars and planets.
Spectroscopy
The development of spectroscopy or spectrum measurement in the 1860s was a great achievement for astronomy. The light of the star passed through a plate known as the grid and was separated on the plate by spectral wavelengths. This helped to create a kind of star map. However, as the image below shows, the spectrum of the Arcturus star had all the spectrum colors of the rainbow, as well as some black lines.
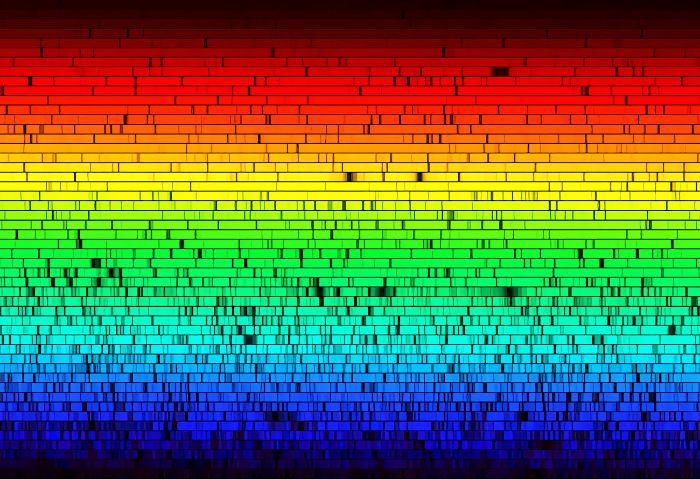

Each set of black lines defined an atomic type. For example, while hydrogen lines always appeared at certain wavelengths, helium lines always appeared in some other group. So spectroscopy made us understand what the stars (and other objects) are actually made of. The spectroscopy also reveals the stars’ relative speeds according to the Solar System.
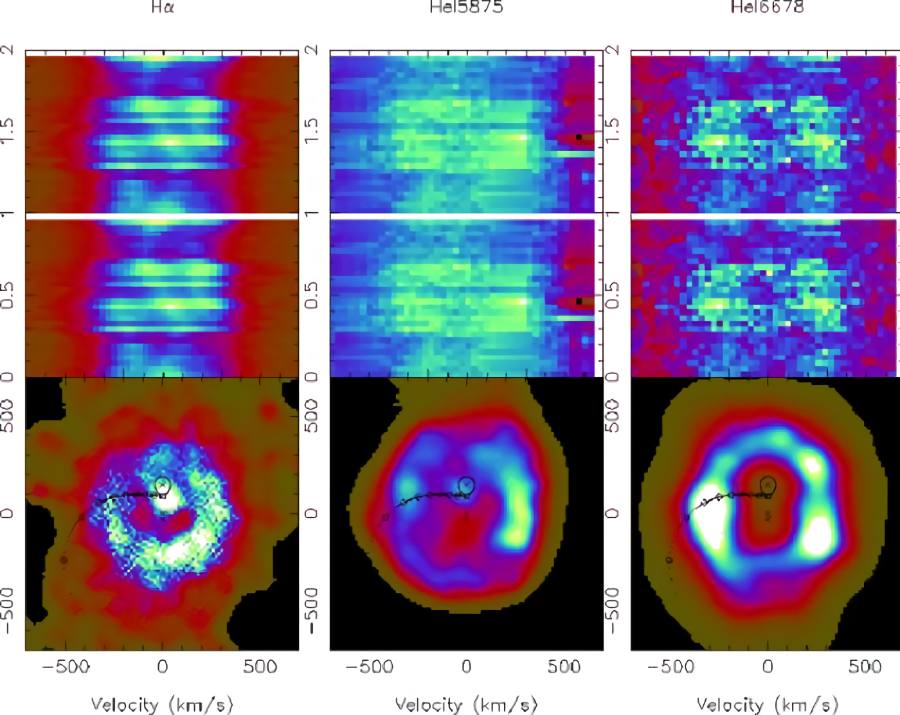
Doppler tomography
Some stars have very large stains on their surface that cover very large areas. Thanks to the method known as Doppler tomography, astronomers have been able to indirectly view the surfaces of these stars since the 1980s. This method is similar to the medical imaging methods that doctors use to see inside the human body.
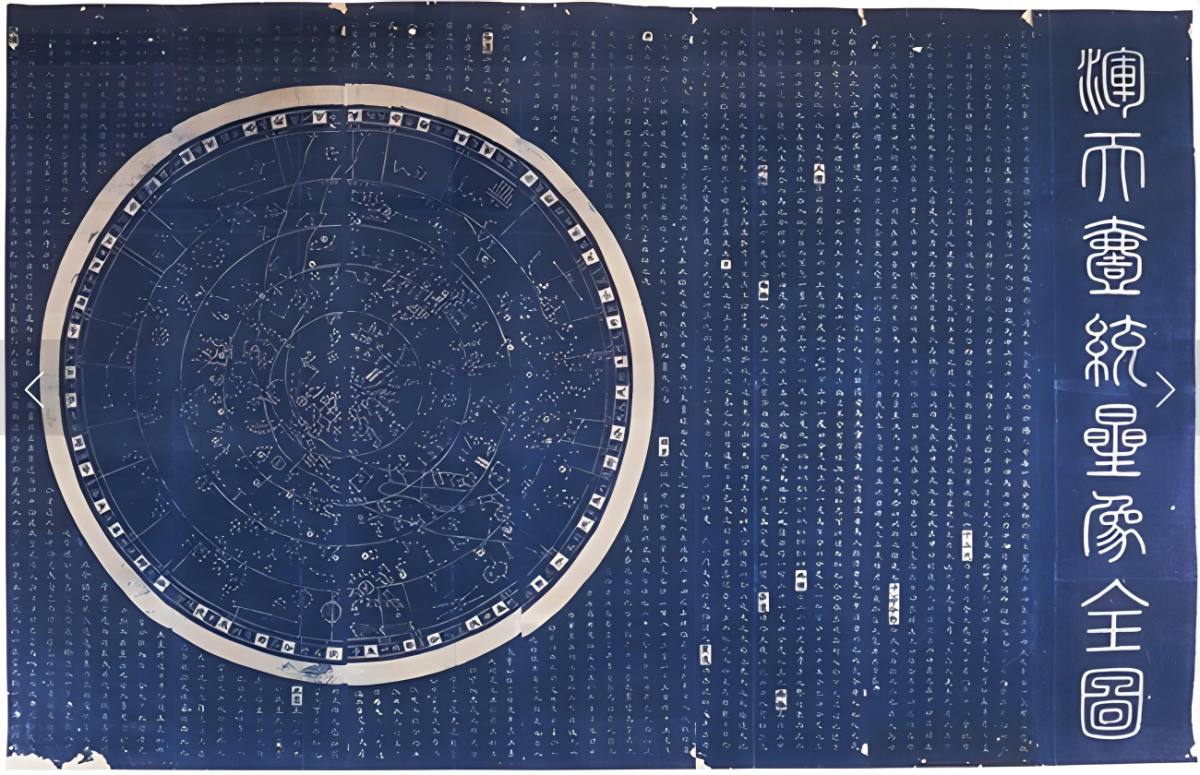
Chinese celestial sphere
The Chinese had long been known as intelligent astronomers, and therefore the Chinese star maps go back centuries. There is evidence that they discovered the sunspots much earlier than the commonly known date of 1611. It was also noted that they recorded the 1054 supernova (SN 1054), resulting in the formation of the Crab Nebula. The 18th-century map below shows 1,464 stars, divided into 283 constellations.

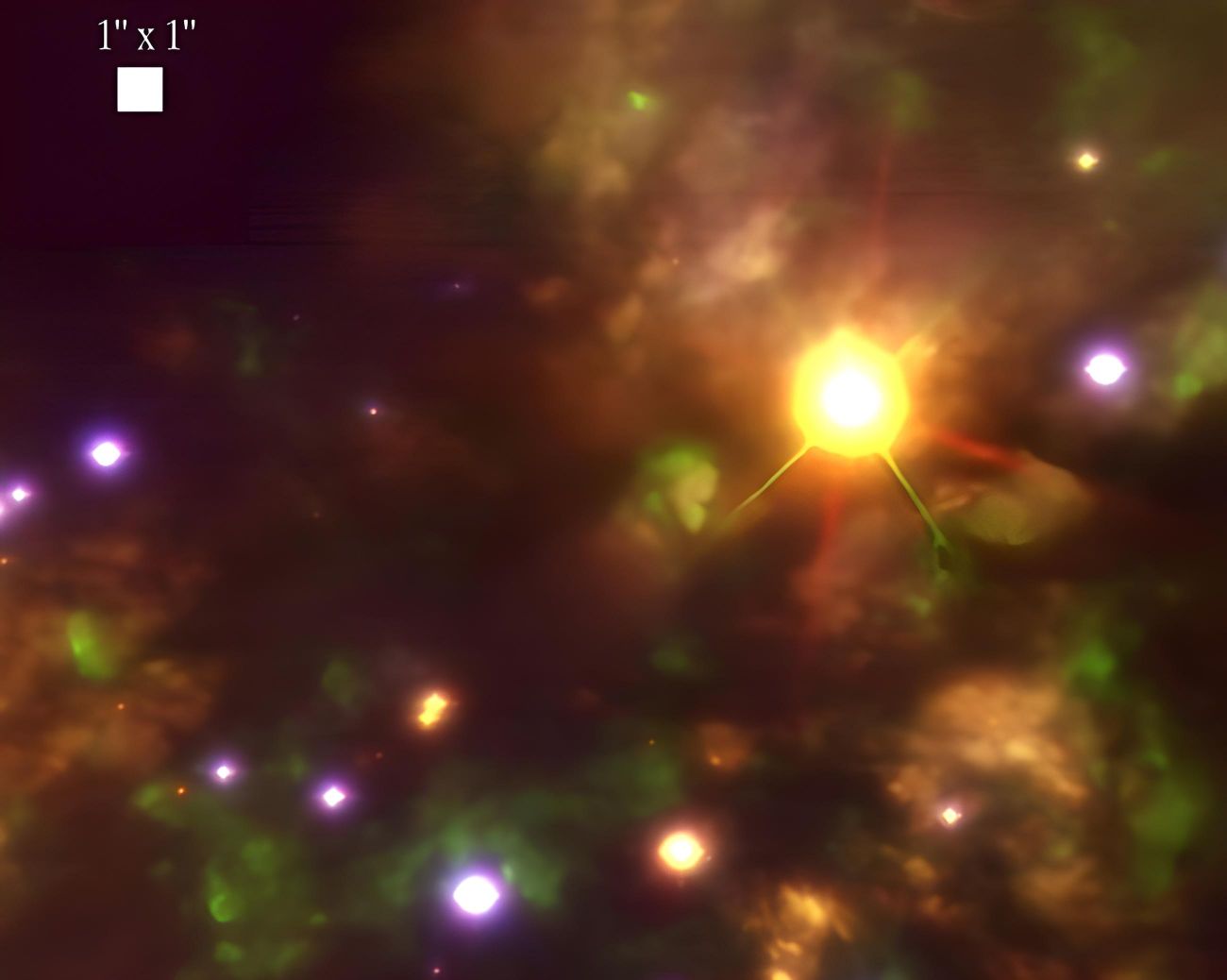
Becklin-Neugebauer object
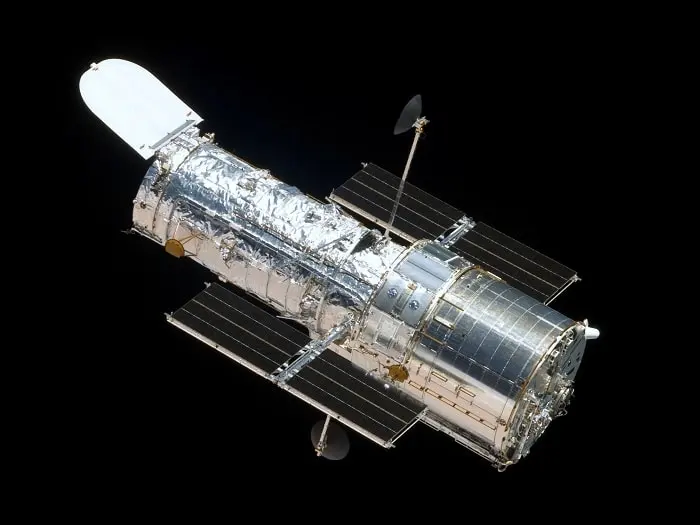
Since many astronomical objects are visible only in the infrared spectrum, it is necessary to go as far as possible in the atmosphere to make more detailed observations. This Hubble Space Telescope image below shows a rather large star in the depths of the Orion Nebula. This infrared radiation source is the Becklin-Neugebauer object itself. The object was discovered in 1966, and it was infrared astronomy’s first major discovery.
The history of stargazing begins with ancient Egypt before Christ, and looking at the size of the discoveries made, it is understood that humanity had been observing the stars for centuries. Today, it is known that every galaxy has billions of different stars.