Sometimes, big stones or boulders from outer space pass over our heads; if their names vary, it’s because they have their own unique characteristics. Then, what are the differences between a comet, an asteroid or a meteorite? The comet is a unique astronomical object, therefore, let’s begin there.
Comets, gaseous strands
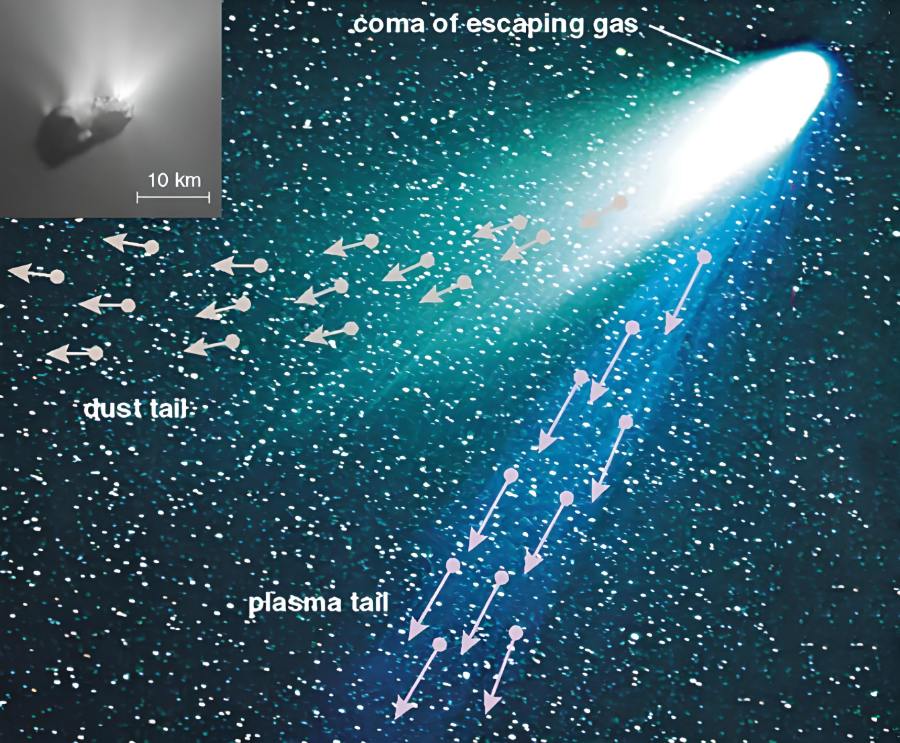

Neowise was the final one seen by the naked eye in the summer of 2020. This extrasolar object was visible for a month in the northern hemisphere sky and originated in the furthest limits of our solar system. The Kuiper Belt, which extends beyond Neptune’s orbit, and the Oort Cloud, a much more distant megasphere, have both been identified by astronomers as a significant comet source. Can we trace the origins of Neowise? What it is, is a mystery. However, it, like the comets that came before it, tends to form in such regions.
So, for some unknown reason, their course suddenly begins to point toward Earth, given their wildly erratic orbit. Comets put on their greatest display when they are closest to the Sun. Their core (which may be as small as a few hundred feet or as large as a few tens of miles is encircled by a hair that splits into two tails, one consisting of dust and colorless gas and the other of hot plasma with a blue color.
The comet “melts” as it approaches the Sun, breaking up into ice rocks and other volatile components, and sending its “hair” trailing behind it for 20–50 million miles (30–80 million kilometers). Comets are a curious point of interest; having been there since the birth of the solar system some 4.5 billion years ago.
Asteroids, debris of planets
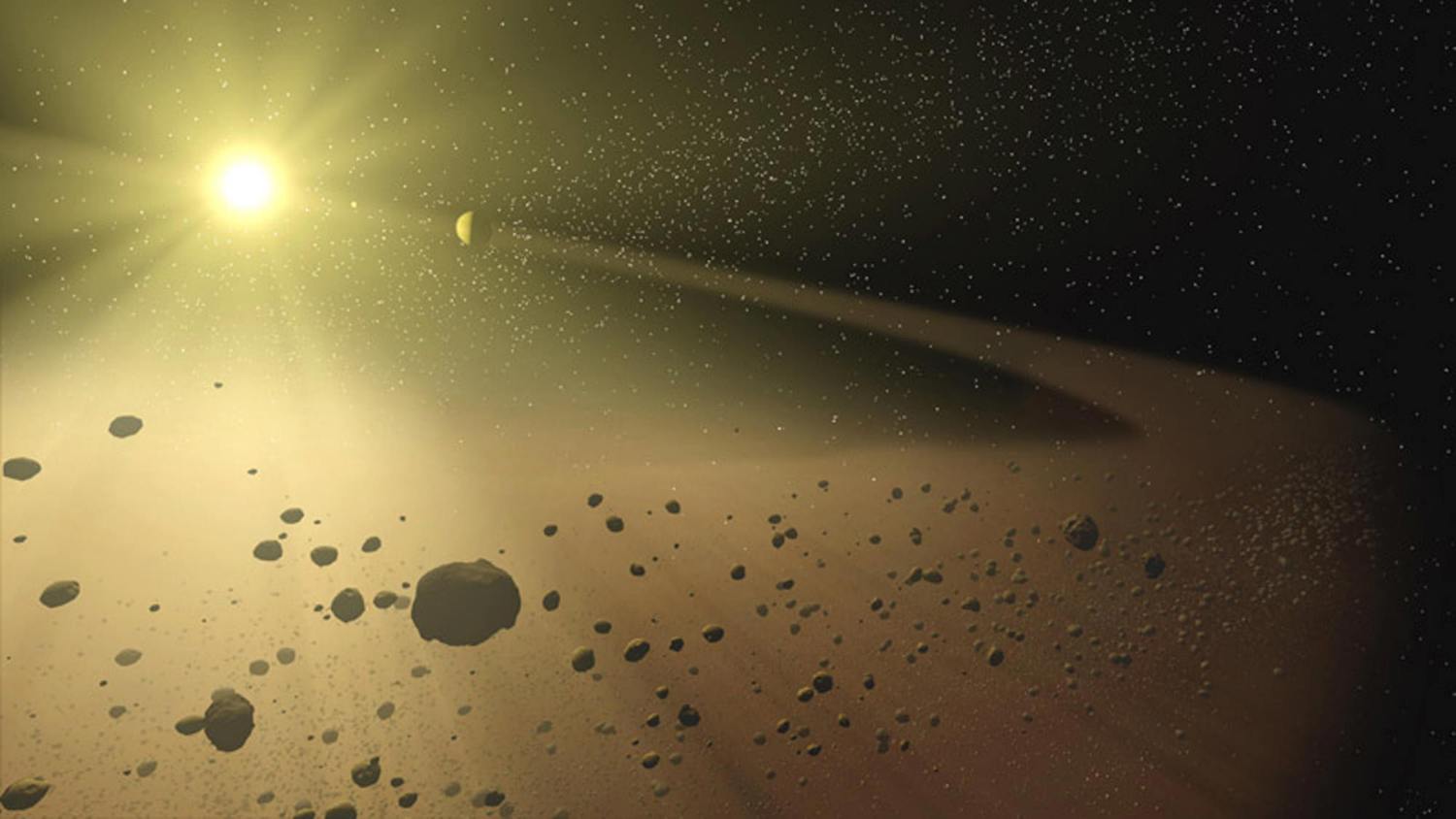

Like comets, asteroids are leftover “debris” from the early days of the solar system. Indeed, the term “planetary leftovers” is commonly used for asteroids. In contrast to comets, however, they are found in the asteroid belt, which extends from Mars to Jupiter. More than a million of those asteroids larger than a mile in diameter have been cataloged so far by astronomers.
Comets are also distinct from regular asteroids because of their unique chemical makeup. Asteroids are essentially “dead” bodies since they are devoid of ice. Carbonaceous, silicate, and metallic families account for the vast majority of all asteroids.
With regard to their behavior, asteroids are capable of venturing outside of their usual range of operation. Some have veered off course and are able to travel through the planetary orbits of objects like the Earth. We refer to them as “NEOs.” The American space agency NASA keeps a careful eye on the 27,500 asteroids of varying sizes that pass within a safe distance of Earth every year.
Nonetheless, comets and asteroids are of intense interest to astronomers since they may hold clues about the solar system’s origin. NASA has sent many probes into space to investigate and perhaps bring back asteroid samples.
Meteors or meteorites
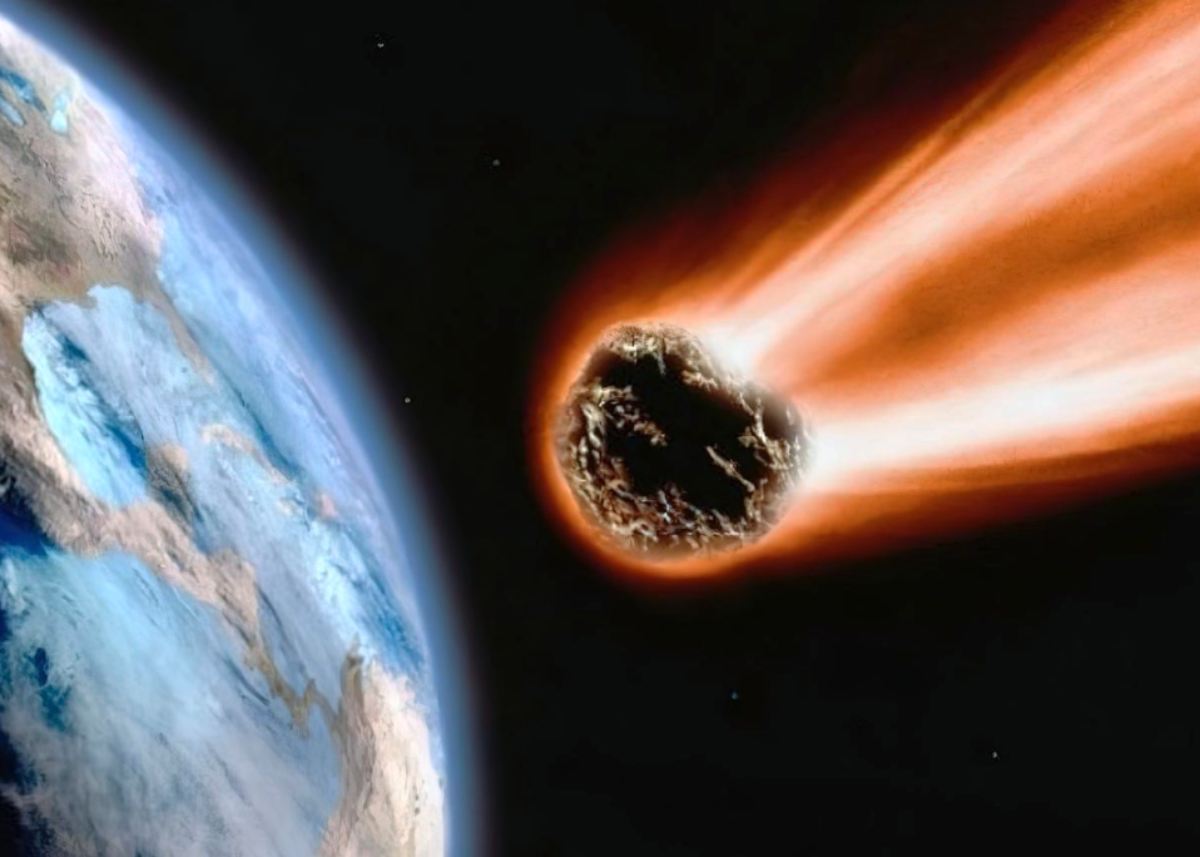

In conclusion, meteorites are asteroid pieces. The size of these objects varies, although they are often considerably smaller than comets or asteroids. Nonetheless, what sets them apart is the fact that they successfully crossed Earth’s atmosphere to land on the planet. A meteor is a body that has somehow failed in its mission. Before reaching the earth, they either burned up or vanished in a brilliant flash of fire.
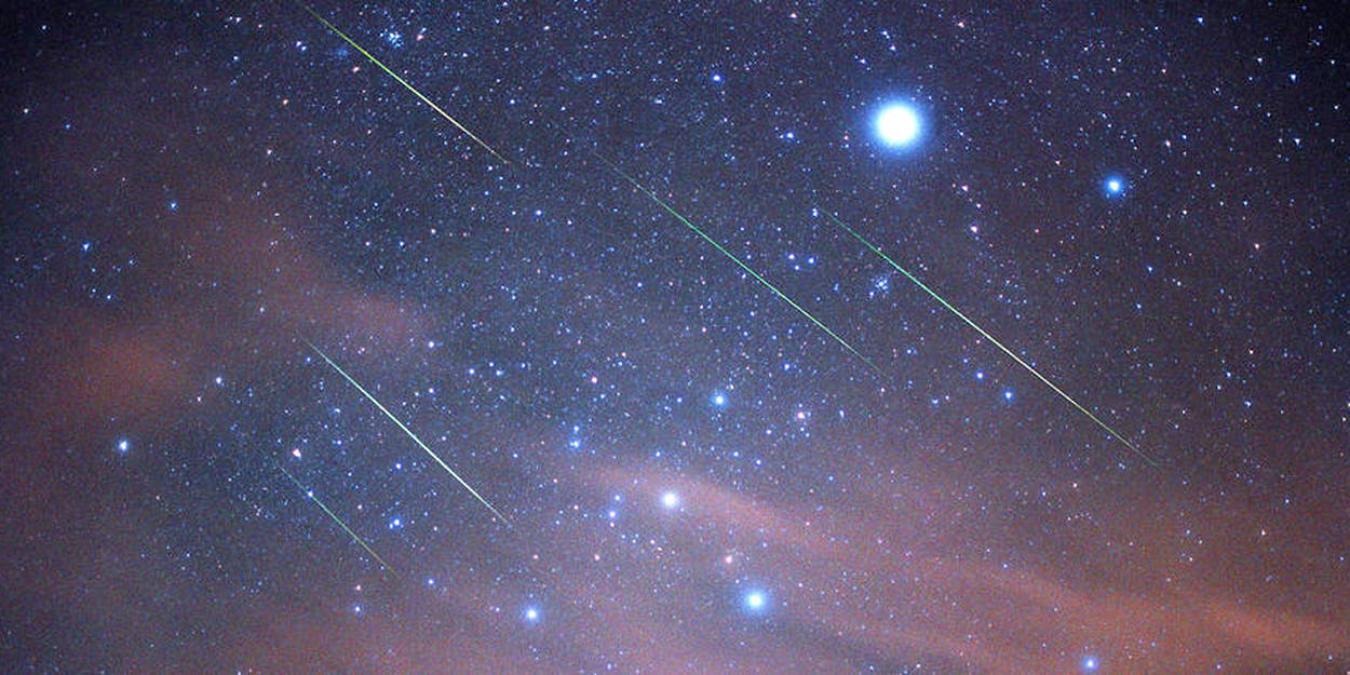
Watch the stars as they streak across the sky. Meteors, not stars, are the ones that burn out. There are two prime times to see this magnificent show: the Geminids in December and the Perseids in August. In the case of meteorites, this occurs considerably more often than you think. The Earth is being “bombarded” with dust or tiny cosmic stones every day. Each day, on average, 230 meteors with a mass of more than 10 grams or 0.35 pounds rain down on Earth, as reported by NASA.