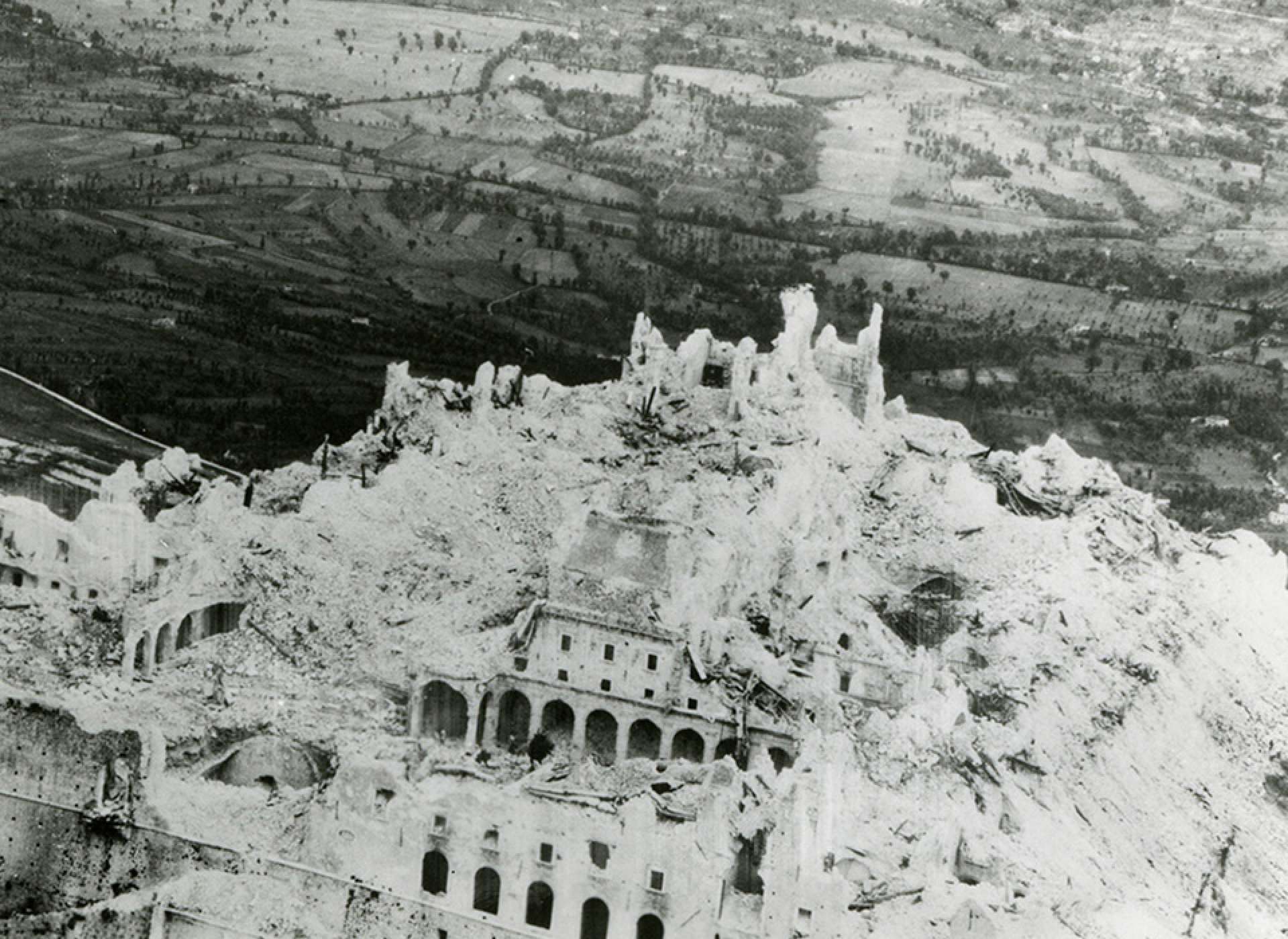
In May of 1944, the Italian Battle of Monte Cassino reached its peak. The Germans sought to block the Allied march on Rome in July 1943, after the Allied arrival in Sicily, by utilizing Rome and the monastery of Cassino as key defense sites. Cassino was the site of one of the deadliest battles of World War II in May, and was a constant target of Allied offensives between November 1943 and the spring of 1944, when the famed monastery was bombed to bits on February 15.
Five Months of Fierce Fighting During the Battle of Monte Cassino

This whole thing started in January of 1944. In July 1943, the Allies landed in Sicily (Operation Husky), then in September 1943, they landed in the south of mainland Italy (Operation Avalanche), beginning their push towards the north of the Peninsula.
Army Group C, led by Marshal Albert Kesselring, fought against the United States Fifth Army (under General Mark W. Clark), the United Kingdom Eighth Army (under Lieutenant-General Oliver Leese), and the Canadian Expeditionary Force (June, 4 divisions, 3 of which were based in North Africa).
“The Smiling Albert” as he was known, had two little armies (the 14th and the 10th), but despite their inferior equipment, he could still rely on elite forces to win. But he utilized the troubled terrain of the battlefield to great effect. The Apennine Mountains run along the middle of the Italian peninsula. And Kesselring had constructed many tiers of defenses surrounding the Apennines, the strongest of which was the Gustav line.
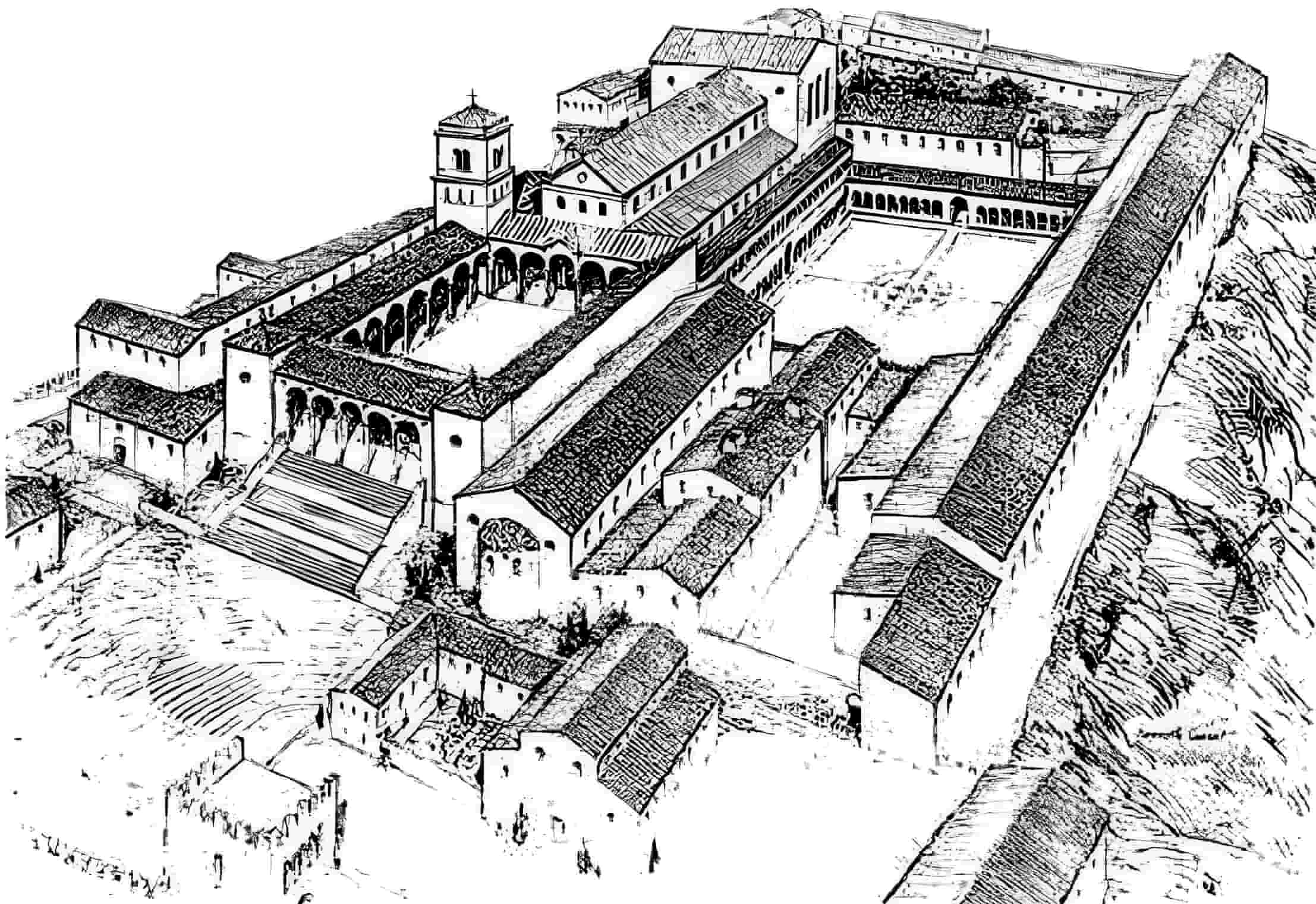

The location of Monte Cassino was the strongest point of the Gustave Line, which the Allies were approaching towards the year’s conclusion. There it protected the primary north-south route, which followed the valley of the Liri River and was the sole legitimate axis of movement towards Rome.
There was a monastery on its peak dating back to the 14th century that looked out over the town of Cassino and posed a significant barrier until it was destroyed by aircraft bombardment.
In order to finally overcome the Gustav Line, the Allies had to repeatedly push through here. All of the attacking divisions were met with heavy opposition by the 14th Panzer Corps and the German parachute battalions (Americans and British, but also French, Indians, New Zealanders, and Poles). Before attempting a landing in the Anzio region (Operation Shingle, January 22nd, 1944), the Allies had to concentrate on shoring up the German defenses.
U.S. General Lucas’ landing force at Anzio was unable to expand its initial foothold and launch a surprise attack on the 14th Armored Division. Despite the successes of the French colonial soldiers, the situation for the Allies seemed hopeless at the start of February 1944, both at Anzio and around Monte Cassino. Between February 15 and February 18, 1944, the Allies launched a second frontal attack against the Gustav Line, but the Germans repelled it once again.
Operation Diadem of the Battle of Monte Cassino

During the following months, the Allied troops reorganized in preparation for a new mission. The French General Alphonse Juin planned the audacious maneuver that became the basis of Operation Diadem (May 11, 1944). The plan was to attack from the southwest, via the Aurunci Mountains, which had previously been thought to be inaccessible to any force, and thereby circumvent the formidable Cassino defenses.
He believed his colonial forces (especially the goumiers and Moroccan riflemen) would be able to move quickly because of their tenacity and the mule caravans that carried all of their supplies.

At the same time, British forces were to cut off access to the town of Cassino by seizing control of the main road, American forces were to provide cover for the French as they advanced to the south, and Polish forces were to be tasked with the herculean task of seizing the monastery atop Monte Cassino. A daring scheme, the inner workings of which Kesselring would never know.
On 11 May, Operation Diadem was launched. The 2nd Moroccan Infantry Division riflemen eventually conquered Mount Majo after a series of very violent opening assaults. Once the Aurunci mountains were traversed, exploitation could begin.
The German high command saw that retaining its soldiers on the present line meant certain encirclement in the face of the onslaught of French mountain troops and a general attack on the remainder of the line. On the 18th, the lock protecting the route to Rome was broken when the Poles took the abbey.
In response to the breakthrough by French elements of the CEF (French Expeditionary Corps under General Juin), Marshal Kesselring, commander-in-chief of Axis troops in Italy, ordered the withdrawal of his forces from this location.
The Liri Valley was opened to the allies, paving the way for the 4 June fall of Rome. For the Germans, the end of the bloodiest combat in the Italian theater marked the beginning of their retirement to the Gothic Line fortifications (north of Florence), which they kept defending until the spring of 1945.
The valor of French colonial forces in North Africa was undoubtedly bolstered in great part by their participation in the famously intense mountain combat the Battle of Monte Cassino.